1. Historical Development
Rugs have long been considered not just utilitarian items but also works of art, with a history that dates back thousands of years. Both Persian and Turkish rugs have played a significant role in the evolution of this textile art form.
Persian Rugs:
The art of Persian rug making is deeply rooted in history, with a tradition that spans over 2,500 years. These exquisite creations have evolved through various stages, each marked by its distinctive characteristics. The history of Persian rugs can be divided into several periods, each of which has contributed to the unique charm of these rugs.
Ancient Persia: The earliest Persian rugs date back to the 5th century BCE, during the Achaemenid Empire. They were primarily utilitarian and often featured geometric designs.

Islamic Period: With the spread of Islam in Persia, rug design began to incorporate intricate floral and arabesque patterns, reflecting the influence of Islamic art and culture.
Safavid Dynasty: The Safavid period (1501-1736) marked a significant turning point in Persian rug design. This era gave birth to the highly coveted Persian “Oriental” rug, characterized by intricate patterns, high knot density, and vibrant colors. The city of Isfahan became a renowned center for rug production during this time.
Qajar Dynasty: The Qajar period (1785-1925) continued the tradition of fine rug craftsmanship, often featuring intricate medallion designs and softer color palettes.
Modern Era: Persian rug production continued to evolve in the modern era. While traditional patterns are still prominent, contemporary Persian rugs often incorporate modern design elements to cater to changing tastes.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs also boast a rich history, with roots stretching back to the nomadic tribes of Central Asia. Over time, these rugs have gone through their own unique evolution.
Central Asian Origins: Turkish rug weaving can be traced back to the Central Asian steppes, where nomadic tribes used them for practical purposes like insulation, flooring, and even as wall hangings. Early Turkish rugs were characterized by simple geometric motifs and bold colors.
Ottoman Empire: The rise of the Ottoman Empire brought about significant changes in Turkish rug making. During this period, Turkish rugs began to incorporate more intricate floral and arabesque patterns, reflecting the artistic influences of the broader Islamic world. The Ottoman Empire produced some of the most well-known and treasured rug designs, including the famous “Hereke” rugs.

Modern Turkey: In contemporary Turkey, the art of rug making continues to thrive, with various regions producing rugs featuring distinct patterns and designs. Traditional Turkish rug motifs are still prevalent, but there’s also a growing trend toward incorporating modern elements to appeal to a global market.
Influence of Dynasties and Political Shifts
The historical development of Persian and Turkish rugs was deeply influenced by the dynasties and political shifts that occurred in their respective regions. These changes left their mark on the designs, materials, and techniques used in rug production.
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs bore the influence of the numerous dynasties that ruled over Persia, shaping their design and quality. The Safavid Dynasty, in particular, played a crucial role in elevating the art of rug making to new heights.
The Safavid rulers were not only great patrons of the arts but also established royal workshops, where master weavers created some of the most intricate and highly prized Persian rugs. Political stability and royal patronage during this period contributed to the flourishing of Persian rug craftsmanship.

Turkish Rugs:
In Turkey, the Ottoman Empire was the dominant force that shaped the development of rug weaving. The Ottomans were known for their appreciation of the arts and their efforts to encourage and promote rug production. This resulted in the creation of some of the most iconic Turkish rug designs.
The end of the Ottoman Empire and the emergence of modern Turkey brought about changes in rug production as the country underwent a shift from a monarchy to a republic. Despite these changes, Turkey has continued to maintain its rich tradition of rug making, blending historical motifs with contemporary elements.

In the following sections of this blog post, we will delve deeper into the distinct characteristics of Persian and Turkish rugs, exploring their unique designs, materials, and craftsmanship.
2. Artistic and Symbolic Elements
Symbolism of Patterns and Colors
Both Persian and Turkish rugs are renowned for their intricate patterns and vibrant colors, each of which carries its own symbolism and significance. These artistic elements not only enhance the beauty of the rugs but also tell unique stories and reflect the cultural heritage of their regions.
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs are often celebrated for their complex and meaningful designs, where patterns and colors hold a deeper significance. Here are some common elements found in Persian rugs:
Floral Patterns: Flowers, leaves, and vines are a common theme in Persian rugs. These floral motifs represent the beauty of nature, growth, and the fleeting nature of life.
Geometric Patterns: Geometric shapes, such as medallions and geometric borders, are also prevalent. These patterns can symbolize the order and harmony of the universe.
Animal Motifs: Persian rugs sometimes feature animal motifs, such as birds or mythical creatures like phoenixes. These animals can symbolize various virtues or characteristics, like freedom and rebirth.
Color Symbolism: Colors in Persian rugs are carefully chosen. Red symbolizes love and wealth, blue represents wisdom, and green stands for life and the natural world. Earthy tones signify humility and purity.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs also incorporate symbolic elements in their designs, often inspired by the rich cultural history of the region:
Mihrab Patterns: Many Turkish rugs feature a “mihrab,” which is a niche shape often seen in mosques. It symbolizes a connection to the divine and spiritual enlightenment.
Gul Motifs: “Gul” patterns are geometric and octagonal shapes commonly found in Turkish rugs. They symbolize protection and are believed to ward off evil spirits.
Color Symbolism: Turkish rugs are known for their use of bright, warm colors. Red, for example, is often associated with passion and love, while blue can represent the sky and the infinite.
Regional Variations in Design
Both Persian and Turkish rugs exhibit a remarkable diversity of designs, influenced by the regions in which they are produced. These regional variations provide insight into the distinct characteristics and histories of these rugs:
Persian Rugs:
Isfahan Rugs: Isfahan, a historic city in Iran, is known for producing high-quality Persian rugs with intricate medallion designs, elaborate floral patterns, and a wide color palette.
Tabriz Rugs: Tabriz, another prominent Persian rug-producing city, is famous for its finely woven, detailed rugs. They often feature motifs like hunting scenes and intricate arabesque patterns.
Kashan Rugs: Kashan rugs are celebrated for their elegant floral designs and fine, detailed weaving. They are known for their classic and timeless beauty.
Turkish Rugs:
Anatolian Rugs: The Anatolian region of Turkey produces a wide range of rug styles, from traditional prayer rugs with mihrab patterns to tribal and village rugs featuring bold geometric designs.
Hereke Rugs: The Hereke region is renowned for producing luxurious, finely woven Turkish rugs. They often feature intricate floral motifs and are prized for their exquisite craftsmanship.
Kilim Rugs: Kilims, or flat-woven rugs, are found throughout Turkey and the surrounding regions. They often display geometric patterns and bold colors, making them versatile and popular choices.
Now, let’s explore the materials and craftsmanship that go into creating these exquisite rugs.
3. Manufacturing Techniques
Weaving Methods (Knotting Techniques)
The production of Persian and Turkish rugs hinges on the weaving techniques employed, and the primary distinction between them lies in the knotting methods.
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs are traditionally woven using one of two primary knot types: the Senneh (asymmetrical) knot and the Ghiordes (symmetrical) knot.
Senneh Knot: Also known as the Persian knot, this technique entails looping the yarn around a single warp thread and passing it behind the adjacent warp thread. It allows for intricate and detailed designs but may be slightly less durable compared to the Ghiordes knot.
Ghiordes Knot: While more common in Turkish rugs, the Ghiordes knot is also utilized in some Persian rug weaving. It involves looping the yarn around two warp threads, resulting in a symmetrical knot that is often deemed more robust.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rug weavers predominantly favor the Ghiordes knot, celebrated for its symmetrical structure, contributing to a uniform appearance.
Material Preparation (Spinning, Dyeing, etc.)
The raw materials and their preparation, including spinning yarn and dyeing, play a pivotal role in the manufacturing process of both Persian and Turkish rugs.
Persian Rugs:
Wool: Persian rugs often feature the use of high-quality, fine wool sourced from sheep, known for its sheen and durability. For more intricate designs in finer rugs, silk may also be employed.
Dyeing: The traditional choice for dyeing Persian rugs is natural dyes, derived from natural sources such as plants, insects, and minerals. These natural dyes provide vibrant, long-lasting colors and contribute to the rugs’ enduring value.
Spinning: Careful spinning is critical to ensuring the yarn’s consistency in thickness and strength, which in turn affects the overall quality of Persian rugs.
Turkish Rugs:
Wool: Turkish rugs are crafted from a variety of wool sources, including sheep, goats, and camels. The choice of wool can influence the texture and appearance of the final rug.
Dyeing: Traditional Turkish rugs typically employ natural dyes, mirroring the Persian tradition. These natural dyes result in rich and warm colors. In contemporary Turkish rug production, synthetic dyes may also be used for cost efficiency.
Spinning: The spinning process in Turkish rug making aims to produce uniform and robust yarn, ensuring the rug’s durability and longevity.
4. Material Utilization
Commonly Used Materials (Wool, Cotton, Silk)
Both Persian and Turkish rugs rely on a selection of materials, with wool, cotton, and silk being the most commonly used.
Wool: Wool is a primary material for both Persian and Turkish rugs. It is prized for its durability, natural luster, and adaptability to intricate designs.
Cotton: Cotton is often used in the foundation of rugs to provide stability and structure. It is commonly found in the warp and weft of these rugs.
Silk: Silk, known for its luxurious appearance and fine texture, is used in more high-end and intricate rug designs, particularly in Persian rugs. It adds a touch of opulence to the final product.
Origin and Quality of Materials
The origin and quality of materials used in rug making significantly impact the final product.
Origin of Materials:
Persian Rugs: Persian rugs often source their materials locally, utilizing the wool from Iranian sheep and the silk produced in Iran. These materials are cherished for their quality and contribute to the authentic nature of Persian rugs.
Turkish Rugs: Turkish rug production similarly relies on domestic sources for its materials. Turkish wool, cotton, and silk are used to maintain the authenticity and regional character of these rugs.
Quality of Materials:
Persian Rugs: Persian rugs are celebrated for their use of fine, high-quality materials. The wool and silk used are often recognized for their exceptional texture and durability.
Turkish Rugs: Turkish rugs, too, prioritize the use of quality materials, with a focus on durability and texture. The materials’ quality influences the rug’s lifespan and aesthetic appeal.
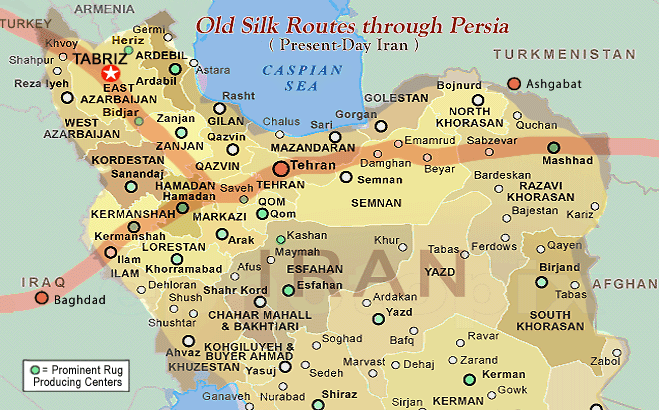
5. Notable Rug Producing Regions
Across the globe, several cities and regions have earned recognition for their exceptional rug production. These locales contribute to the rich tapestry of rug-making traditions, with each bearing its own unique characteristics and design aesthetics.
Prominent Persian Rug-Making Cities/Regions:
Isfahan: Isfahan, an ancient city in Iran, is renowned for its production of high-quality Persian rugs. These rugs often feature intricate medallion designs and a diverse color palette.
Tabriz: Tabriz, another prominent city in Iran, is famous for finely woven rugs that incorporate motifs like hunting scenes and elaborate arabesque patterns.
Kashan: The city of Kashan produces rugs known for their elegant floral patterns and fine craftsmanship, resulting in classic and timeless beauty.
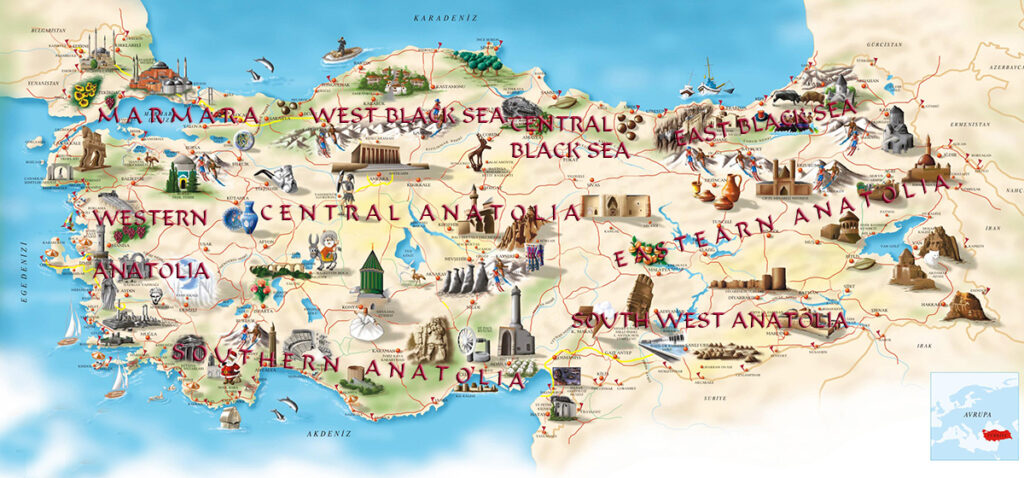
Prominent Turkish Rug-Making Cities/Regions:
Anatolia: The Anatolian region of Turkey is celebrated for its diverse range of rug styles, from traditional prayer rugs with mihrab patterns to bold geometric designs in tribal and village rugs.
Hereke: Hereke, a small town near Istanbul, is renowned for its luxurious, finely woven Turkish rugs. These often feature intricate floral motifs and are prized for their exquisite craftsmanship.
Kilim: Kilims, or flat-woven rugs, are found throughout Turkey and surrounding regions. They are known for their use of geometric patterns and bold colors, making them versatile and popular choices.
Distinct Characteristics of Regional Rugs
The distinct characteristics of regional rugs are shaped by the cultural and historical influences of their locales.
Persian Rugs:
Isfahan Rugs: Known for intricate medallion designs and a wide color palette, Isfahan rugs often exude a sense of regal elegance.
Tabriz Rugs: Tabriz rugs showcase finely woven designs with motifs like hunting scenes and elaborate arabesque patterns, reflecting the city’s rich artistic heritage.
Kashan Rugs: Kashan rugs are distinguished by their elegant floral patterns and fine craftsmanship, making them a timeless choice.
Turkish Rugs:
Anatolian Rugs: Anatolian rugs are celebrated for their diversity, ranging from traditional prayer rugs with mihrab patterns to vibrant and bold geometric designs found in tribal and village rugs.
Hereke Rugs: Hereke rugs stand out for their luxurious quality, featuring intricate floral motifs and meticulous craftsmanship, often designed for a more opulent setting.
Kilim Rugs: Kilim rugs are characterized by their flat-woven style and distinctive geometric patterns, offering a more casual and versatile appeal.
6. Authenticity and Imitation
Identifying Authentic Persian and Turkish Rugs
Distinguishing authentic Persian and Turkish rugs from imitations or forgeries is crucial when making a purchase.
Authentic Persian Rugs:
Look for a signature: Many authentic Persian rugs have the weaver’s signature woven into the design.
Inspect the knotting: Persian rugs typically use Senneh or Ghiordes knots, which should be meticulously executed.

Examine materials: High-quality wool or silk, as well as natural dyes, are hallmarks of genuine Persian rugs.
Seek expert guidance: Consulting with rug experts or reputable dealers can help verify authenticity.
Authentic Turkish Rugs:
Check for the Ghiordes knot: Most Turkish rugs use this knotting technique, which should be uniform and well-executed.

Assess the materials: Authentic Turkish rugs use quality wool, cotton, or silk, and may incorporate natural dyes.
Regional characteristics: Familiarize yourself with the distinct features of rugs from Anatolia, Hereke, or Kilim, depending on the region of origin.
Seek professional appraisal: If in doubt, consider having the rug appraised by an expert to confirm its authenticity.
Dealing with Replicas and Forgeries
To avoid purchasing replicas and forgeries, it’s important to be cautious and conduct thorough research:
Purchase from reputable dealers: Choose well-established and reputable rug dealers who are known for their authenticity.
Study the rug: Carefully inspect the rug’s materials, knotting techniques, and design, and be wary of deals that seem too good to be true.
Request documentation: Ask for certificates of authenticity or provenance from the seller, which can help verify the rug’s origins.
Consult experts: If uncertain, seek the opinion of experienced rug appraisers who can provide guidance on authenticity.
By understanding the distinct features of authentic rugs and taking precautions, you can confidently navigate the market and ensure you’re acquiring a genuine piece of art.
Which is better, Persian or Turkish rug?
The debate between Persian and Turkish rugs has been a long-standing one, and it’s not as simple as declaring one superior to the other. The choice between these two exquisite rug traditions ultimately depends on your personal preferences, needs, and the intended use of the rug.
Here, we’ll delve into various factors to consider when determining which type of rug might be better for you.
1. Aesthetic Appeal
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs are known for their intricate and often elaborate designs, featuring everything from floral motifs to geometric patterns.
The wide array of colors and the use of natural dyes create a rich and timeless visual appeal.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs often lean toward bold, geometric patterns and vibrant colors, which can lend a more energetic and contemporary feel to a space.
Kilim rugs, a type of Turkish rug, offer a flat-woven style with distinctive, often tribal, designs.
2. Material and Quality
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs are crafted with a focus on quality materials. High-grade wool and silk, along with the use of natural dyes, contribute to their durability and lasting beauty.
The fine knotting techniques used in Persian rug making ensure intricate designs and intricate details.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs are also known for their use of quality materials, including wool, cotton, and sometimes silk.
The Ghiordes knot, common in Turkish rugs, is favored for its strength and durability.
3. Regional Variations
Persian Rugs:
Persian rugs offer a diverse range of designs based on the region of origin. Isfahan, Tabriz, and Kashan are just a few of the cities known for their unique styles.
Regional variations in Persian rugs cater to different tastes, from classic elegance to more modern aesthetics.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs similarly exhibit regional variations, with Anatolia, Hereke, and Kilim rugs each offering distinct characteristics.
The choice among these regional styles can reflect your preference for traditional or more contemporary designs.
4. Budget and Investment
Persian Rugs:
Authentic Persian rugs can be significant investments due to the high-quality materials, intricate designs, and cultural significance.
However, there are affordable options available, especially when considering less intricate designs.
Turkish Rugs:
Turkish rugs, including Kilim rugs, offer a broader price range, making them more accessible to a variety of budgets.
You can find both high-end and budget-friendly options in the world of Turkish rugs.
In conclusion, the choice between Persian and Turkish rugs is not a matter of one being definitively better than the other. Instead, it’s about selecting the one that aligns with your aesthetic preferences, your budget, and the overall style of your living space.
Whether you’re drawn to the timeless charm of Persian rugs or the vibrant energy of Turkish rugs, the ultimate decision is a matter of personal taste. Explore both traditions, feel the textures, and let the artistry of these rugs inspire your choice.